I hear you've studied architecture? Come on, make a short chain system.
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Three Link Generation Methods
- The Redirection Process
- Cache Optimization
- Designing for High Availability
- Postscript
**01 Introduction
**1) Background
This is a system design question in my interview with the department of “Byte Shake”, the position is “back-end senior development engineer”, asked in the second interview. At the beginning, the interviewer smiled and asked me to introduce myself, and then talked about the project.
After talking about the project flawlessly and writing an algorithm question, the interviewer started to ask questions.
The interviewer began to ask: young man, resume inside wrote familiar with architectural design is not it, then you know program design ‘three high’ refers to what?
I thought to myself, that is not due to the programmer’s system is not reliable, the leadership is not the right person, every day overtime to change the BUG, resulting in a young age are high blood fat, high blood pressure and high blood sugar!
However, since this is an interview, the leader is certainly not willing to listen to this, so I answered: program three high, that is, the system design needs to consider the high concurrency, high performance and high availability:
- High concurrency is in the process of system development, the need to ensure that the system can simultaneously process many requests in parallel;
- High performance means that the program needs to take up as little memory and CPU as possible and process requests as fast as possible;
- High Availability usually describes that the system is not serviceable for a short period of time, for example, no more than 31.5 seconds of downtime throughout the year, commonly known as 6 9s, which means that availability is guaranteed for 99.9999% of the time.
So, the interviewer nodded slightly, thinking that the young man is not bad, since this can not be difficult for you, then I have to come up with a big trick, let’s have a system design questions!
**2) Statement of Requirements
As we all know, when business scenarios need to send the user a network address or QR code, due to the length of the address is relatively long, usually in order to take up fewer resources and improve the user experience. For example, the address of the Google search term “computer” is as follows:
1 | https://www.google.com/search?q=%E8%AE%A1%E7%AE%97%E6%9C%BA&ei=KNZ5Y7y4MpiW-AaI4LSACw&ved=0ahUKEwi87MGgnbz7AhUYC94KHQgwDbAQ4dUDCBA&uact=5&oq=%E8%AE%A1%E7%AE%97%E6%9C%BA&gs_lcp=Cgxnd3Mtd2l6LXNlcnAQAzIECAAQQzIFCAAQgAQyBQgAEIAEMgUIABCABDIFCC4QgAQyBQgAEIAEMgUIABCABDIFCAAQgAQyBQgAEIAEMgUIABCABDoKCAAQRxDWBBCwAzoLCC4QgAQQxwEQ0QM6FggAEOoCELQCEIoDELcDENQDEOUCGAE6BwguENQCEENKBAhBGABKBAhGGABQpBZYzSVglydoA3ABeACAAZ0DiAGdD5IBCTAuNy4xLjAuMZgBAKABAbABCsgBCsABAdoBBAgBGAc&sclient=gws-wiz-serp |
Obviously, it is not “decent” to send this long list of URLs to users. Moreover, when encountering some systems with word limits, such as microblogging posts with word limits, it is definitely not possible to send such a long link address. In general, most of the SMS links are short links:
So, in order to improve the user experience, as well as the daily business needs. We need to design a short link generation system, in addition to the realization of business functions, we have to serve the national network address. With such a large number of users, how should the data be stored and how should high concurrency be handled?
02 Three methods of link generation
1) Requirements Analysis
I thought to myself, this interviewer looks “kind eyes” and smiling, but the topic is not simple, this type of system needs to be considered too many points, absolutely can not be taken lightly.
So, I was from the link generation, URL access, cache optimization and high availability of four aspects of the design.
First of all, the generation of short link address, you can consider using UUID or self-incrementing ID. for each long link to short link address, must generate a globally unique short link value, otherwise there will be a conflict. So, short links are characterized by:
- The amount of data storage is large, the national URL is at least a million short link addresses need to be generated every day;
- Concurrency is not small, encountered at the same time to access the system, according to 3600 seconds a day to calculate, the average number of requests per second at least thousands;
- short links can not be repeated, otherwise it will cause data access conflicts.
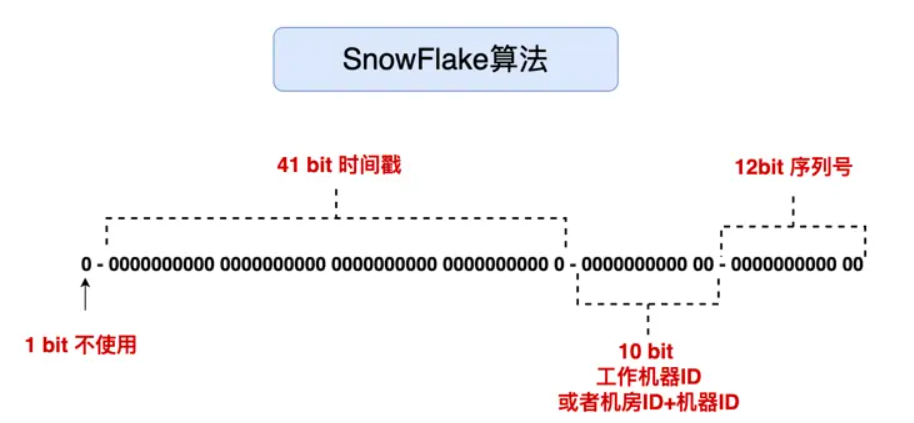
**2) Snowflake Algorithm
First of all, to generate short links, you can use the snowflake algorithm + hash to achieve.
The snowflake algorithm is a unique number generated in a distributed scenario based on timestamps, different machine IDs, and sequence numbers. Its advantage is that it is simple and easy to use as you go.
Through the snowflake algorithm to get the unique number, and then hash mapping, the number will be converted to a random string, if the short chain string is longer, you can directly take the first 6 bits. However, because the result of hash mapping may conflict, so the hash algorithm is more demanding.
2) 62 Progressive Number Generation of Short Links
In addition to the snowflake algorithm, you can also use the number of 62 (A-Za-z0-9) to generate short link addresses. First get a self-incrementing ID, and then convert this value to a string of hexadecimal (a-zA-Z0-9), a billion digits converted to just five or six (100 million -> zAL6e).
The short link server domain name, and this string for splicing, you can get the URL of the short link, such as: t.cn/zAL6e.
And generating the self-incrementing ID needs to consider the performance impact and concurrency security, so we can make an issuer through Redis’ incr command, which is an atomic operation, so we don’t have to worry about the security of the numbers. And Redis is an in-memory operation, so it is quite efficient.
3) Random number + Bloom filter
In addition to incrementing the ID, we can also generate random numbers and then convert to hexadecimal to generate short links. However, since the random numbers may be duplicated, we need to use Bloom filters to de-duplicate them.
The Bloom filter is a cleverly designed data structure that works by hashing a value multiple times, mapping it to different bit bits and recording it. When the new value is used, the same hash function is used to compare whether there is a value on each bit bit: if there is no value on any of these bit bits, the number is unique; otherwise, it may not be unique.
Of course, this may produce a misjudgment, ** Bloom filter can certainly find duplicate values, but ** ** may also be non-duplicated values judged as duplicates **, the misjudgment rate of roughly 0.05%, is an acceptable range, and the Bloom filter is extremely efficient.
Therefore, through the Bloom filter, we can determine whether the generated random number is duplicated or not: if it is duplicated, a new one will be generated; if it is not duplicated, it will be deposited into the Bloom filter and the database, thus guaranteeing that the random number fetched each time is unique.
**4) Store the short link to the database **
When storing the database, different databases may be chosen because of the amount of inventory and technology stack. However, since MySQL is used more in the company department and the current topic does not mention technology selection, we choose MySQL as the persistent database.
Whenever a short link is generated, the mapping relationship from short link to long link needs to be stored in MySQL with a unique index, i.e. zAL6e -> real URL.
03 Redirection process
When the browser accesses the short link service, it fetches the original URL based on the short link address and then redirects the URL. We usually have two redirection methods:
- One is to return a 301 response code to the browser for permanent redirection, so that it can directly access the real URL address in the future;
- One is a 302 temporary redirection, so that the browser currently this time to visit the real URL, but subsequent requests are still based on the short chain address access.
Although the 301 browser only one request, the follow-up can be directly from the browser to get a long link, this method can improve access speed, but it can not count the number of visits to the short link.
So according to the business needs, we usually choose 302 redirection.
04 Cache Design
Since the short link is distributed to multiple users, it may be accessed multiple times in a short period of time, so the long link can be put into redis cache after writing/fetching it from MySQL.
1) Add to cache
And, the correspondence between short and long links is usually not modified frequently, so the consistency between the database and the cache is ensured by a simple Bypass Cache Mode:
- When reading (Read) data, if the cache is not hit, the DB is read first, and the data is taken out of the DB and put into the cache, while the response is returned;
- When writing (Write) data, first update the DB, then delete the cache.
When the user needs to generate a short link, first go to this mapping table to see if there is a corresponding short link address. If there is one, return it directly and increase the expiration time of the key-value by one hour; if not, regenerate it and store the corresponding relationship in the mapping table.
The cache elimination strategy can be chosen:
- LRU: Least Recently Used, the short-link address that has been read and written recently as hot data can always exist in the cache, eliminating those short-link keys that have not been accessed for a long time;
- LFU: Least Frequently Used, the recent least frequently used algorithm, the recent short chain address with high access frequency can be used as hot data, eliminating those short chain keys with lower access frequency.
- Cache penetration
However, the use of cache can not prevent some anomalies, such as “cache penetration”. The so-called cache penetration is to query a cache and database do not exist in the short link, if the concurrency is very large, it will lead to all the cache does not exist in the request to hit the MySQL server, resulting in the server can not handle so many requests and blocked, or even crash.
Therefore, in order to prevent the miscreants from attacking the server in a similar way as “cache-penetration”, we can adopt two methods to deal with it:
- Cache the non-existing short link address, the key is the short link address, the value value is empty, the expiration time can be set to a shorter time;
- Bloom filter will have a short link hash many times after the storage, when there is a short link request, first through the Bloom filter to determine whether the address exists in the database; if not, it means that the database does not exist in the address, it will be returned directly.
05 High Availability Design
Since caching and database persistence rely on Redis and MySQL, high availability of MySQL and Redis must be guaranteed.
- MySQL High Availability
The MySQL database uses master-slave replication to separate reads and writes; the master node is used for writes and the slave node is used for reads, and it can be keptalived to achieve high availability.
The principle of Keepalived is to use virtual IP to detect multiple nodes in the portal, select a hot standby server as the master server, and assign it a virtual IP through which external requests can access the database.
At the same time, Keepalived detects the availability status of multiple nodes in real time, and when a server is found to be down or faulty, it will be kicked out of the cluster. If this server is the master, keepalived will trigger an election operation to elect another server from the server cluster to be the master and assign it the same virtual IP to complete the failover.
And, with Keepalived’s support, these operations don’t require human involvement, just the repair of the failed machine.
- Redis High Availability
Because of the high concurrency of big data scenarios, write requests all fall on the master node of Redis, the pressure is too great. If you insist on increasing memory and CPUs in this vertical expansion, then a machine facing the gradual increase in disk IO, network and other pressures, which will also affect performance.
So Redis uses cluster mode to realize data sharding. Moreover, a sentinel mechanism is added to ensure the high availability of the cluster. Its basic principle is that the sentinel nodes monitor all the master and slave nodes in the cluster, when the master node is down or after a failure, the sentinel nodes will mark it as subjective offline; when enough sentinel nodes will mark the Redis master node as subjective offline, it will be changed to the state of the Objective offline.
At this point, the sentinel nodes elect a lead sentinel through an election mechanism to perform a failover operation on the Redis master node to guarantee the high availability of the Redis cluster, and this entire process requires no human intervention.
- System Fault Tolerance
Before the service goes live, it needs to do a full assessment of the business volume, as well as performance testing. Do a good job of limiting the flow, fusion and service degradation logic, for example: the use of token bucket algorithm to achieve the limitation of the flow, hystrix framework to do the fusion, and will be commonly used configurations into the configuration center that can be hot update, so as to facilitate the pair of its real-time changes.
When the business volume is too large, the synchronous task is changed to asynchronous task processing. Through these service governance solutions to make the system more stable.
06 Postscript
When I finished the last word, the interviewer looked at me with admiration and doubt in his eyes. I thought that he should have been impressed by my performance, and that the interview should have been a sure thing.
However, surprisingly, the interviewer did not comment on the architectural design, but only looked at me and said, “That’s it for today’s interview, do you have anything you want to ask?”
Now, it was my turn to be shocked, so did I pass or not? But to give a sentence ah, so I asked, “through this interview, you think I have what aspects need to be improved?”
“Algorithms and projects need to be practiced more, but I found a good thing about you.” The interviewer laughed and then said, “You’re pretty good at memorizing eight-legged essays!”
My hanging heart finally dropped, and I thought to myself, “Oh, that’s steady~”